Construction of functional curdlan hydrogels with bio-inspired polydopamine for synergistic periodontal antibacterial therapeutics
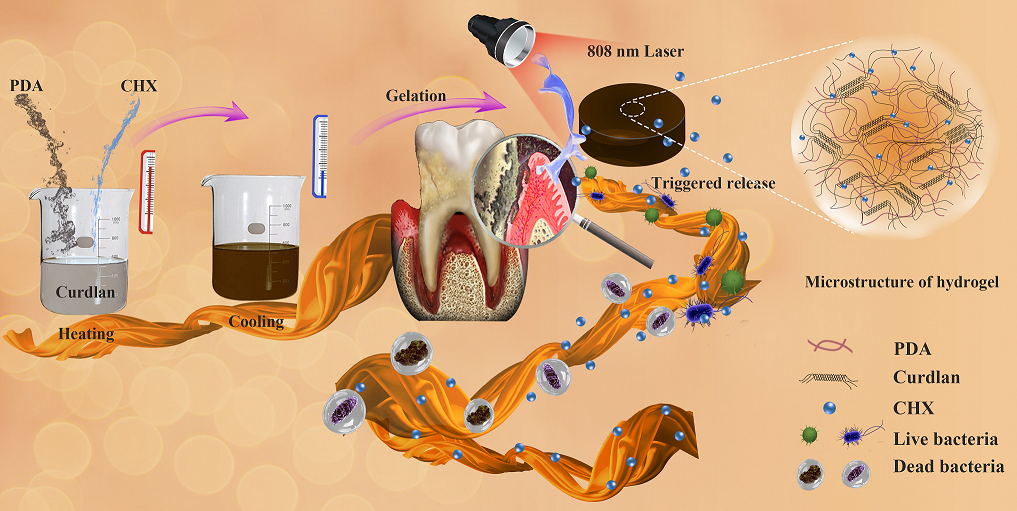
Periodontitis could not only compromise life qualities sharply, but also hazard the systematic fitness due to bacterial-related factors. In this study, the facile engineering of a functional hydrogel carrier composed of curdlan polysaccharide and polydopamine (PDA) was reported for periodontal treatment. The physiochemical evaluations of curdlan and PDA composite hydrogel (CP) proved its competent properties associated with concentration of PDA. We have systematically assessed the designed hydrogels for the biocompatible experiments in vitro and found that these hydrogels exhibited good cytocompatibility. Moreover, photothermal performance upon near infrared light (NIR) exposure was conducted and eventually indicated the best matches for antibacterial application (CP3). The acetate chlorhexidine (CHX) was chosen as a model antimicrobial and the drug release profiles demonstrated that the triggered release of entrapped CHX could be nicely controlled by NIR. The optimized bacteriostatic rate could reach 99.9%. Overall, we aimed to provide a new alternative synergistic antibacterial strategy for periodontal treatment by combining photothermal effect and chemical antimicrobial simultaneously. This work was published in the Carbohydrate Polymers (IF:6.044)
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800833 and 21977081), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science of Foundation of China (Z19H180001), the Wenzhou Medical University and Wenzhou Institute of Biomaterials & Engineering (WIBEZD2017001-03).
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800833 and 21977081), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science of Foundation of China (Z19H180001), the Wenzhou Medical University and Wenzhou Institute of Biomaterials & Engineering (WIBEZD2017001-03).

 Intelligent nanomaterial delivery gene drug system
Intelligent nanomaterial delivery gene drug system Cooperative treatment of nano-drugs
Cooperative treatment of nano-drugs Biomedical tissue engineering
Biomedical tissue engineering Construction and application of integrated nanomaterials for diagnosis and treatment
Construction and application of integrated nanomaterials for diagnosis and treatment