- Newsroom
- Research Progress
- Academic Events
- Join Us
Smart Contact Lens with Dual-Sensing Platform for Monitoring Intraocular Pressure and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9
2022-07-07
Recently, Wang’s group constructed a dual-function optical contact lens sensor to achieve non-invasive detection of intraocular pressure (IOP) and biomolecules. The related research result was published in Advanced Science under the title of Smart Contact Lens with Dual-Sensing Platform for Monitoring Intraocular Pressure and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9. This research provided a basis for tele-medicine for the monitoring and treatment of ocular diseases such as glaucoma and dry eye by constructing a dual-function sensor on contact lens and using structural optics and Raman spectroscopy to achieve non-invasive detection of IOP and biomolecules.
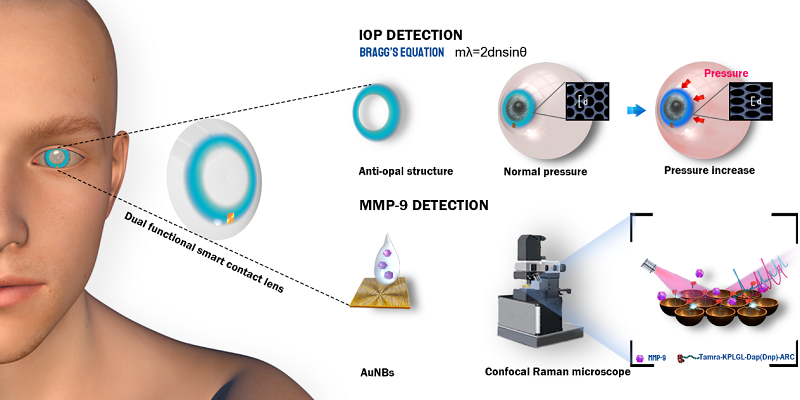
Glaucoma is one of the major blindness diseases in China. More than half of patients with glaucoma are unaware of their disease but have lost some of their retinal ganglion cells by the time of diagnosis, and the damage is irreversible. Early detection and diagnosis are therefore essential for the treatment of glaucoma. In the risk assessment of glaucoma, in addition to the common IOP test, there is a need to detect the relevant biomolecules and to provide a simple measurement method. Since contact lens is in direct contact with the eye, it is expected that biosensors can be integrated into contact lenses to achieve real-time non-invasive diagnosis and health monitoring for a variety of diseases.
Based on this, this work reported an optical-based dual-function smart contact lens sensor for IOP monitoring and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) detection, both of which were key indicators associated with ocular diseases such as glaucoma and dry eye. This work utilized the color change of the anti-opal structure on the contact lens for dynamic monitoring of IOP, which could better cover the physiological IOP range (10-21 mmHg). In addition, by combining the surface-enhanced Raman substrate with the contact lens, the quantitative analysis of MMP-9 in tears was achieved, and compared with other related works for IOP or MMP-9 detection alone, this smart contact lens was able to achieve dual detection of IOP and MMP-9 at a high- performance level. Thus, the smart contact lens sensor developed in this work provided a convenient, non-invasive and remote medical platform for disease diagnosis and laid the foundation for integrating more functions into contact lenses in the future.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202104738