Decoupled gelatin methacrylamide (DGM)
2020-11-27 16:15:01
Niu's paper (Highly substituted decoupled gelatin methacrylamide free of hydrolabile methacrylate impurities: an optimum choice for long-term stability and good cytocompatibility) has been accepted in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules ( 中科院SCI期刊分1区, 2020年, IF: 5.162)
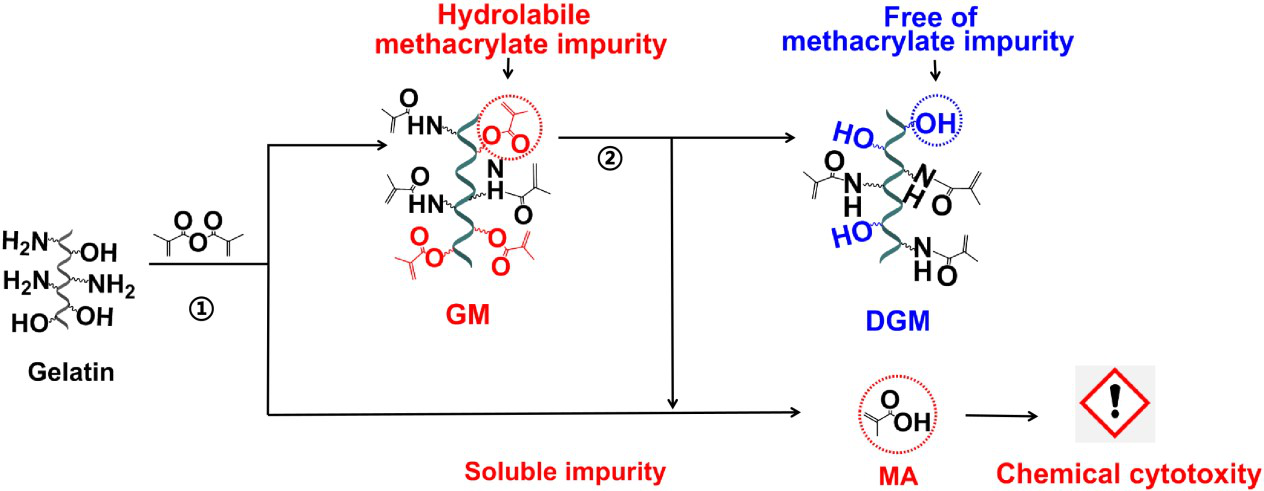
Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA; GM) contains impurities, including hydrolabile photosensitive methacrylate groups or soluble methacrylic acid (MA), which could be potentially detrimental to its in vitro and in vivo applications. To date, the influence of GM photocurable side chains on the cytotoxicity and ambient structural stability has remained to be investigated. Here, we successfully separated highly substituted decoupled gelatin methacrylamide (DGM) from GM via removing methacrylate impurities in order to evaluate its stability, cell viability, and cell toxicity, compared to GM, DGM plus soluble MA, and soluble MA. The photocurable methacrylate groups in GM were hydrolytically labile in neutral solutions, changing into soluble MA over time; on the other hand, the photocurable methacrylamide groups in DGM remained intact under the same conditions. Soluble MA was found to decrease cell viability in a dose dependent manner and caused severe cell toxicity at above 10 mg/mL. DGM plus MA started to impair cell viability at a 25 mg/mL concentration. DGM exhibited excellent cell viability and little cell toxicity across the treat concentrations (0.1 – 25 mg/mL). DGM without hydrolabile methacrylate and cytotoxic MA impurities could be a better choice for long term stability and good cell compatibility for bioapplications including bioprinting and cell encapsulation.
Highlights
1. The influence of GM/DGM photocurable side chains on the cytotoxicity and ambient structural stability was investigated.
2. Soluble impurities caused severe cell toxicity in a dose-dependent manner.
3. DGM could offer a better choice for long-term stability and good cell compatibility.